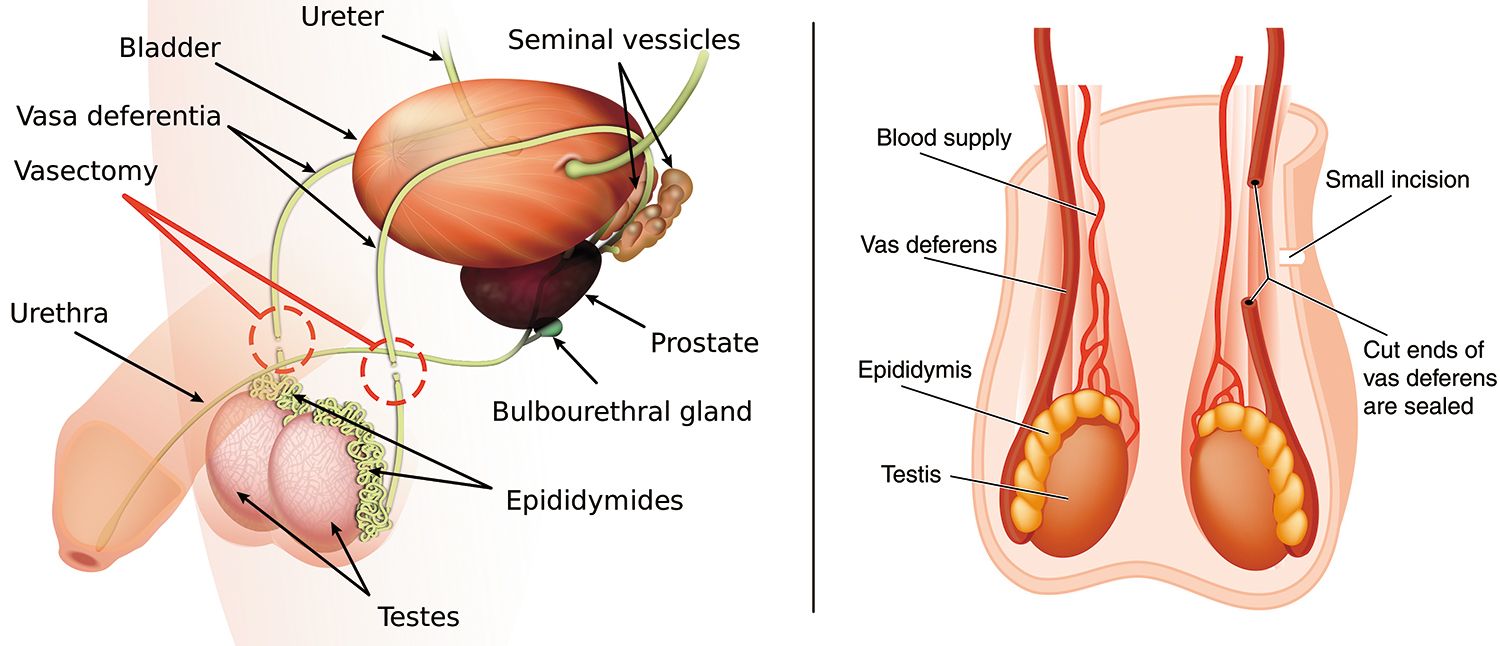
Vasectomy

A vasectomy is a permanent form of contraception. It iis a minor surgical procedure that involves cutting the 2 small tubes (vas deferens) that carry sperm from the testes to the penis.
After a vasectomy, your semen is the same, but it has no sperm in it.
Vasectomy is a safe, effective, and permanent form of contraception.
How effective is vasectomy?
A vasectomy is over 99% effective.
However, while it is rare, a vasectomy may fail, and you may stay fertile or become fertile again. This can happen if the tubes are not blocked off, grow back together, or if a third tube exists. Usually, this is picked up when the sperm count is done three months after the operation. However, it can occur at any time, even years after the vasectomy.
Is vasectomy right for me?
A vasectomy is a highly effective permanent method of birth control. It is suitable if you are sure you do not want to have children in the future. If you change your mind, a vasectomy can be difficult to reverse, especially if the procedure was done a long time ago.
If you are in a relationship and considering a vasectomy, it is critival to discuss this with your partner before deciding. However, you do not need permission from your partner to have a vasectomy.
How is vasectomy done?
A vasectomy involves a simple surgical procedure that cuts the vas deferens- the 2 small tubes that carry sperm from the testes to where semen is stored.
It takes about 15 to 40 minutes to perform. It is done using an injection of local anaesthetic to numb the area. Some doctors and clinics also offer light sedation, which means you are in a light sleep during the procedure. This will usually involve an extra cost.
The local anaesthetic can be a little uncomfortable when it is first given, and there may be a little sensation during the procedure, but it should not be painful.
A small opening is made in the front of the scrotum (below the base of the penis), with either a scalpel (Scalpel method) or small tweezer (No scalpel method).
Both the vas deferens are then found and cut. Sometimes a small part of each vas deferens is removed. The opening in the skin of the scrotum is then closed with a stitch or by pressing the skin edges together.
What happens after the procedure?
You will usually spend up to 2 hours in the clinic. As the local anaesthetic wears off, there can be some tenderness and discomfort in the scrotum and groin. This can be managed with rest, oral pain relief (such as paracetamol), cold packs, and wearing firm, supportive underwear.
You should rest as much as possible the first day, preferably with your groin elevated to reduce swelling. Minimise any time standing or walking around.
If you have a job that involves mostly sitting, you can return to work the following day if you wish to. You shoulf still wear supportive underwear and use cold packs to help with healing during the first few days.
However, a long recovery time may be needed before doing any exercide or if your job is physically strenuous. Please discuss this with your provider.
When is the vasectomy effective?
Sperm can be present in the semen for up to three months after a vasectomy and can take about twenty ejaculations to clear. You need to use additional contraception until you have had a sperm test three months following the procedure.
Where do the sperm go?
Sperm continue to be produced in the testes after the operation, but they are harmlessly re-absorbed by the body.
When is it ok to have sex again afterwards?
Sexual activity can be resumed whenever it feels comfortable to do so. However, you will need to use contraception until the vasectomy becomes effective.
Remember, a vasectomy does not provide any protection from sexually transmissible infections, so if you are concerned about this, you will need to use condoms.
Does sex or orgasm feel different after a vasectomy?
When the small amount of swelling and tenderness has settled, any sexual activity, orgasm, and ejaculation will feel the same as before.
Will my ejaculate change?
No, sperm only make up a tiny part of the ejaculate (semen), so there will be no change in the volume or appearance of your ejaculate.
Will a vasectomy affect my hormones or my appearance?
A vasectomy does not involve removing the testes, does not affect your hormones, will not affect your ability to produce semen, and does not change sexual function, appearance, or characteristics in any way. The only change is that there are no sperm in the ejaculate.
What are the possible complications from a vasectomy?
Vasectomy is a safe and straightforward procedure. However, it is common to experience some tenderness following the operation. You may also experience minor bruising and swelling, lasting a few days. As mentioned, rest, ice packs, oral pain relief, and supportive underwear will help to minimise these symptoms.
Possible complications include:
A small number of people experience bleeding or infection after a vasectomy. Rest, support of the scrotum, pain relief, and antibiotics will resolve most problems quickly.
Occasionally, sperm can leak from the ends of the cut tubes and produce small, hard lumps at the operation site. These are considered harmless and usually do not cause any problems.
Over time, some people may form antibodies to their sperm after the operation. However, these do not appear to affect any other part of the body or cause disease or discomfort. These antibodies may be one of the reasons why some people who have had a vasectomy reversal cannot recover their fertility.
Very rarely, discomfort in the scrotum may persist following vasectomy. While this usually settles with time, occasionally, it does not, and further surgery may be needed to relieve this discomfort.
Extremely rarely, the spontaneous re-joining of the tube may occur, leading to sperm in the semen.
Can a vasectomy be reversed?
A vasectomy is considered permanent. Sometimes, it is possible to re-join the tubes that have been cut. However, even if this can be done, there is no guarantee that your fertility will return. The chance of a successful reversal also decreases over time.
If you are considering a vasectomy, consider it a permanent decision. If you think there is any possibility that you may want to be fertile in the future, vasectomy may not be suitable for you.
Where can I have a vasectomy?
Vasectomy is performed by some GPs, specialist urologists, or at some sexual health centres. Ask your local doctor or call Sexual Health & Family Planning ACT on 02 6247 3077 for more details and contact information.
References