Condoms

What are condoms?
Condoms are worn during sexual activity to prevent sexually transmissible infections and as a contraceptive method to prevent pregnancy. A condom is a physical barrier that stops body fluids (e.g., semen, vaginal fluids) from passing between sexual partners. There are two different kinds of condom available, the external (male) condom and the internal (female) condom.
External (Male) Condoms
What are external condoms made of?
External condoms are made of thin, strong latex rubber or polyurethane.
How do you use them?
They are used by being rolled onto the erect penis before vaginal, anal, or oral sex. A condom can only be used once then needs to be discarded in the bin.
How effective are external condoms as a contraception?
As a contraceptive method external condoms are 98% effective with perfect use, and 88% effective with typical use. Perfect use means using a condom correctly every time you have sex and using it the whole time. If not used correctly and consistently, the failure rate will be higher.
What are the advantages of external condoms?
- They provide protection against sexually transmissible infections (STIs).
- They can be used as needed.
- They are easy to get from supermarkets, pharmacies, adult shops, and vending machines.
- They are not too expensive.
- There are no significant medical risks or side effects.
- They can be used in combination with other contraceptive methods, such as the contraceptive pill, to increase that method’s effectiveness.
- They can be used with fertility awareness methods to reduce the risk of pregnancy.
What are the disadvantages of external condoms?
- A small number of people are sensitive to latex or lubricant. (Non-latex condoms are available for people with latex allergies).
- The interruption to sexual activity can be a concern for some people.
- Some people complain of reduced sensitivity during sexual activity.
- They can break or slip off.
- Some people may experience difficulties with erections (this can sometimes be helped by practising using condoms before any sexual activity with a partner, especially for younger people).
- People whose erections are less firm may find it a little difficult to use external condoms.

Always check your Condoms have not expired. A condom's expiration date can usually be found on both the box and the individual wrapper.
Why is personal lubrication important when using external condoms?
Lubrication is the wetness that makes penetration more comfortable during intercourse. While most condoms already have some lubrication, using additional water-based lubricant is a good idea. This will increase comfort and help prevent breakages. Water-based lubricants are available from pharmacies and supermarkets; several brands are available, so find one that suits you.
Oil-based lubricants can weaken latex condoms and increase the risk that the condom will break so should not be used. Oil based lubricants include petroleum jelly (e.g., Vaseline), cooking oil, baby oil, suntan oil, massage oil, hand lotions, or creams.
Why do external condoms slip or break?
A condom may slip or break if:
- It is not put on correctly.
- There is not enough lubrication during sexual intercourse.
- An oil-based lubricant is used.
- A vaginal thrush treatment that is oil-based is used.
Check with your pharmacist and use a water-based treatment. - It is torn by fingernails, jewellery, or teeth.
- Sexual intercourse is prolonged or very vigorous.
- The penis becomes soft before withdrawal.
- The penis and condom are not held securely when withdrawing.
- The condom is too big or too small for the penis.
- The latex is weakened when past its use-by date or exposed to heat.
What should i do if a condom slips or breaks?
Emergency contraception can be used to help prevent pregnancy if a condom slips or breaks. It is taken by the partner at risk of becoming pregnant, should be used within 72 hours, and the sooner it is used the better.
In the ACT emergency contraception can be obtained from most chemists, the Walk-in Centres, SHFPACT, and Canberra Sexual Health Centre.
If your sexual partner is a new or casual partner, you should consider having a sexual health check for sexually transmissible infections. You can do this at SHFPACT, at Canberra Sexual Health Centre or with your GP.
If you feel you might be at risk of exposure to HIV then you may need medication to reduce the risk of becoming infected. This medication is called PEP. PEP needs to be taken within 72 hours of exposure.
If you think you may need PEP please contact Canberra Sexual Health Centre on 02 51242184 or go to your local hospital emergency department if it is after hours. See SHFPACT’s PrEP and PEP information brochure for more information about this.
Where are condoms available?
External condoms are available from pharmacies, supermarkets, convenience stores, vending machines, adult shops, and online. They come in different shapes, thicknesses, flavours, textures, sizes, and colours.
Adult shops can assist with less common sizes if you are having difficulty with fit or comfort wearing a condom.
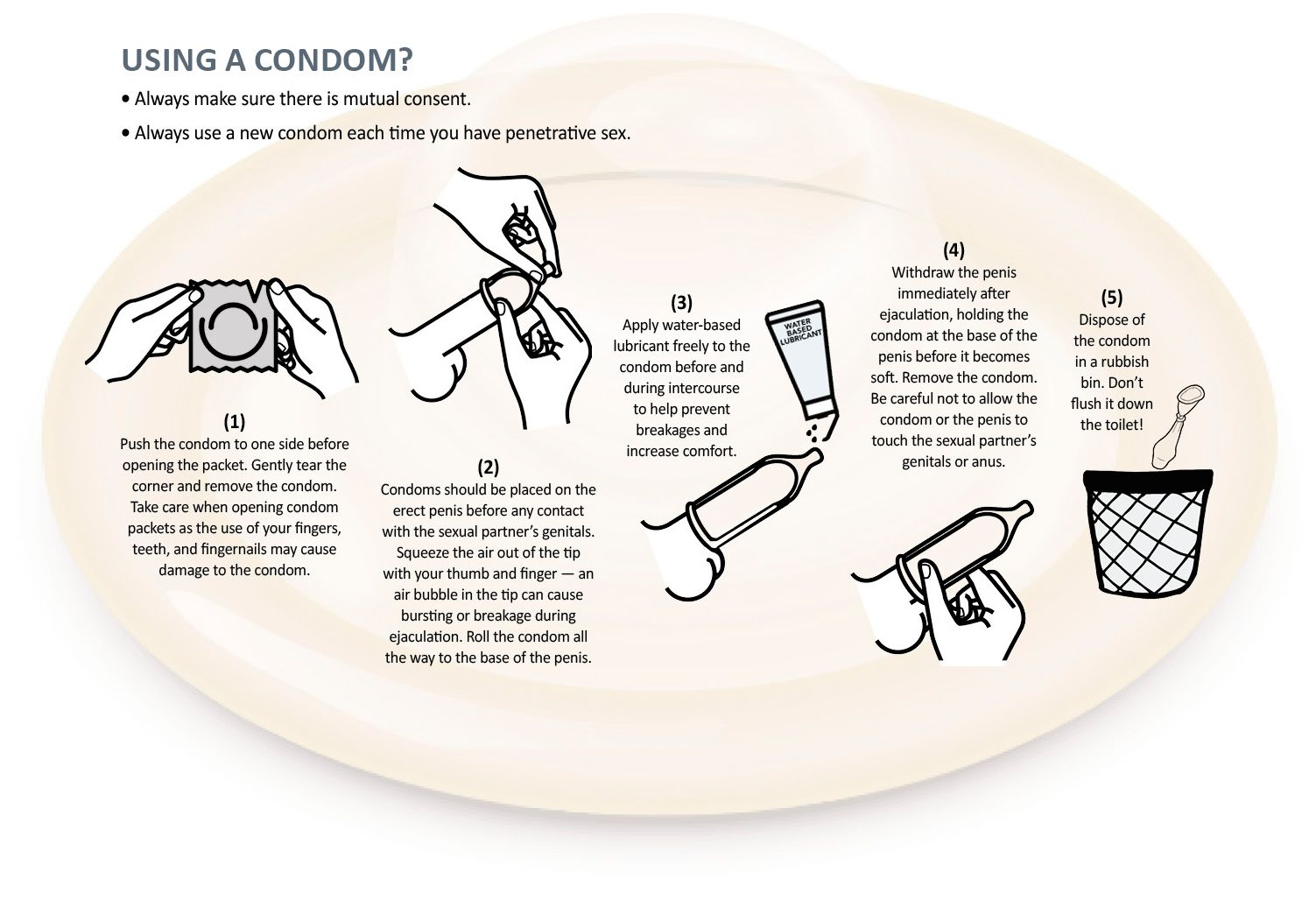
How do I use a condom?
- Always make sure there is mutual consent.
- Always use a new condom each time you have penetrative sex.
Internal (Female) Condoms
What are internal condoms made of?
Internal condoms are made of thin, soft non-latex rubber called nitrile.
How do they work?
They work by covering the cervix, vagina and some of the vulva and preventing the exchange of body fluids.
How effective are internal condoms as contraception?
As a contraceptive method they are 95% effective with perfect use, and 79% effective with typical use. Perfect use means using a condom correctly every time you have sex and using it the whole time. If not used correctly and consistently, the failure rate will be higher.
What are the advantages of internal condoms?
- They provide protection against sexually transmissible infections (STIs).
- They cover the vulva which provides extra protection from STIs.
- They can be used as needed.
- They can be used with any kind of lubricant.
- There are no significant medical risks or side effects.
- The penis does not have to be erect and may remain in the vagina within the condom after ejaculation.
- The material becomes warm which can be pleasurable.
- The outer ring may stimulate the clitoris making sex more pleasurable.

What are the disadvantages of internal condoms?
- They have a higher failure rate than most other contraceptive methods.
- They usually need to be purchased online.
- They are more expensive then the external condom.
Where are internal condoms available?
Internal condoms are available to buy online.